Introduction:
In this article i am going to explain the difference between Array and Arraylist in C#.
Arrays:
Arrays are strongly typed collection of same datatype.Generally in arrays we will store values with index basis that will start with zero. If we want to access values from arrays we need to pass index values.These arrays are of specified length that cannot be change during runtime.
Declaration:
To declare the array use "[]" brackets after data type and then assign the fixed length or fixed size to an array as shown below
static void Main()
{
string[] myArray = new string[3];
myArray
[0] = "Welcome";
myArray
[1] = "to my";
myArray
[1] = "Blog";
}
Above code shows that we
have declared a String type array size of 3 (Means we can store only 3 string values in that array).
ArrayList:
Array lists are not strongly type collection.It stores a collection of values from different data types or same data types.
Array list size will increase or decrease dynamically it can take any size of values from any data type. These Array lists will be accessible with “System.Collections” namespace. If the values stored in collection are of different data types then type cast is must.
Array list size will increase or decrease dynamically it can take any size of values from any data type. These Array lists will be accessible with “System.Collections” namespace. If the values stored in collection are of different data types then type cast is must.
Declaration:
To add values to an array-list you can call "Add" method of Array-List to keep adding values continuously
static void Main()
{
ArrayList aryList = new ArrayList();
aryList.Add(123); // Added Integer value
aryList.Add("C-Sharp"); // Added string value
aryList.Add(DateTime.Now); // Added DateTime
}
Note : If the values stored in collection are of different data types then type cast is must.
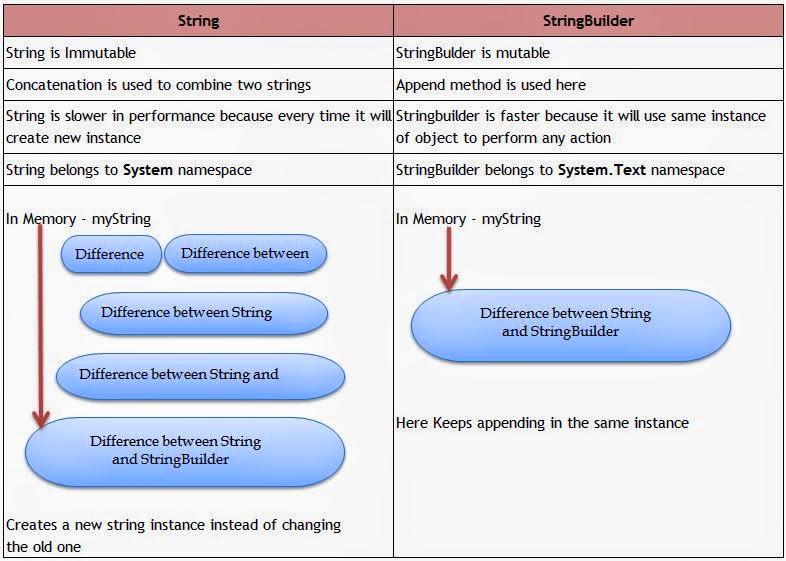
For better understanding check the below table